class ab amplifier advantages and disadvantages
Other than these advantages Class A amplifier is easy to construct with a single-device component and minimum parts count. Emitter resistors absorb output power.
Class Ab Amplifiers Electronics Lab Com
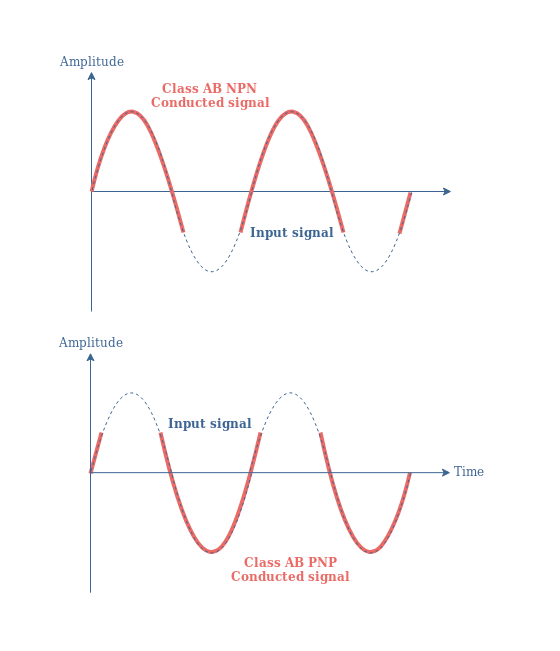
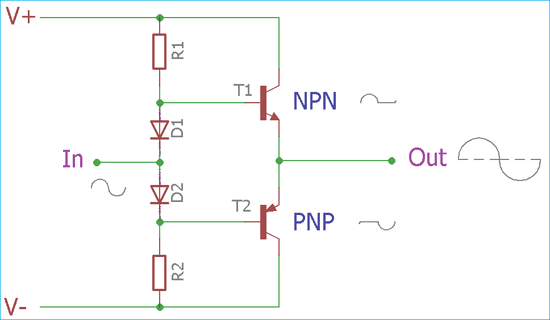
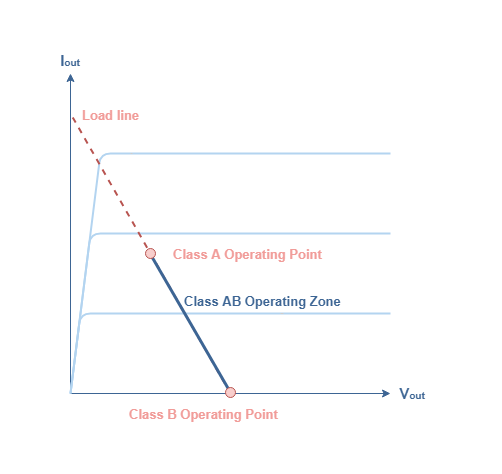
Hence in the class AB amplifier design each of the push-pull transistors is conducting slightly more than the half cycle of conduction in class B but much less than the full cycle of conduction of class A.

. We all know that the more powerful an amplifier is the heavier it. Power dissipation for low signal levels higher than Class B. The reason is that Class AB amplifiers have idle current that runs through the power transistors 10 - 20 milliamps even when there is no audio signal while Class B amplifiers do not idle.
Whereas class D amplifiers start with an input signal and then output signal looks like larger and shorter pulses. Discover thousands of brands. The copper wiring of the class A amplifier is believed to be responsible for the bulky feeling a class A amplifier has.
Power conversion efficiency similar to Class B DISADVANTAGES. First one for the amplification of the Voltage signal Second one for the amplification of the current. Disadvantages of Class AB Amplifiers.
In my point of view class AB audio amplifiers have the following advantages. Temperature matching will be needed more so. If emitter degeneration resistors are not used.
Due to continuous conducting nature the class A amplifier introduce high power loss. Little signal in big signal out. Ad Explore The Best Selection of Musical Instruments Equipment.
No distortion of sound and gives completely clear and good sound. The circuit is simple frequency loan small instant distortion. The disadvantage is that efficiency drops rapidly down towards Class A levels.
The first trick is to inject a little bit of current into the stageso the devices are never fully off this is called class AB and the majority of class B amplifers are actually classAB. The conduction angle of Class AB amplifier is in between 1800 to 3600 which is depending on the bias point. Class AB operation improves on Class B linearity.
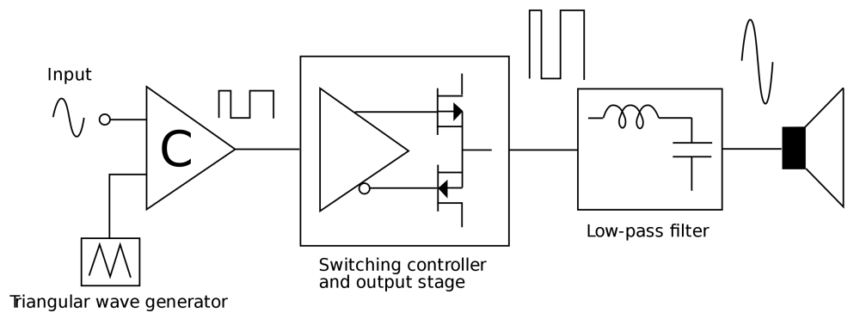
Class D power amplifier speakers may appear distorted for some reason. In short it is making a larger identical signal. Examples of a Class AB Amplifier.
The signal is amplified instantaneously because the tune does not need to wake up. The tube is ready at all times to amplify the signal. Also they have DC components in output as the load is directly coupled.
Also due to high linearity Class A amplifier provides distortion and noises. Ad Shop Now for Amps from Top Brands to Power Your Home or Car Speakers. A 30 watt Class A amp can provide louder sound than a Class AB amp with equal power.
There is a list of advantages and disavantages of the most common audio amplifiers topologies. The advantage of the small bias voltage is to give in. Read customer reviews.
The disadvantage is rather minorClass AB dissipates slightly more power and heat. The next trick is to match the power devices closely. The primary disadvantage over Class AB is a lower efficiency because the tubes are on longer.
Disadvantages of Class D amplifiers. Benefits of Class AB Amplifiers. In the second stage i have used Class AB with the resistor biased.
Class AB makes the input signal and output signal identical and every step of the way. Class A power amplifier advantages. More on time means the tubes will burn out quicker than those in Class B but not as fast as those in Class A.
Despite the advantages and high linearity certainly it has many limitations. Hi-Fi quality sound Simpler design if well designed. Very low distortion THD usually less than 01 at medium output power Linear behaviour.
Class AB Disadvantages. The advantages of Class AB over Class B is much lower crossover distortion. During the initial connection and final shutdown of the power transistor of the Class D power amplifier the potential close to the ground will fluctuate which will increase the noise.
After that we can create a pcb circuit and save the gerber file in order to get fabrication. The advantages of Class A amplifiers are no crossover distortion and switching distortion and the harmonic components are mainly even harmonics. Good channels range available.
Gain of the non-inverting amplifier is 1 RFR2 where RF and R2 shown in the Image. Class A or conventional amplifiers are very reliable but they tend to be bulky is very discouraging. Lowest Price Guaranteed With 45-Day Matching.
No need of coupling transformers. Since the active devices are slightly pre-biased there will be a small amount of collector current flowing and this is the reason behind the slightly reduced efficiency. Class AB amplifiers offer less efficiency than Class B amplifiers.
Class AB power amplifiers are slightly inefficient than the Class B configurations but far better in terms of distortion when compared to Class A configurations. Advantages And Disadvantages Of Amp Classes.

Class Ab Amplifier Circuit Working Advantages Disadvantages
What Is The Difference Between Class Ab And Class D Amplifiers Missing Remote

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers
Classes Of Power Amplifiers Class A B Ab C D Amplifiers Explained
Class Ab Amplifiers Electronics Lab Com

Pdf Amplifier Alphabet Soup Part I Class A Ab B And C

The Classes And Classification Of Amplifiers And Its Applications

Class Ab Amplifier Circuit Working Advantages Disadvantages

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers
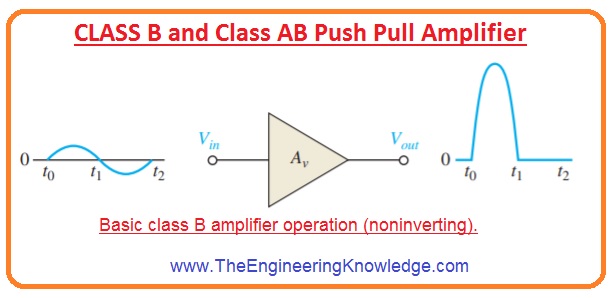
Class B And Class Ab Push Pull Amplifier The Engineering Knowledge

Class B And Class Ab Push Pull Amplifier The Engineering Knowledge
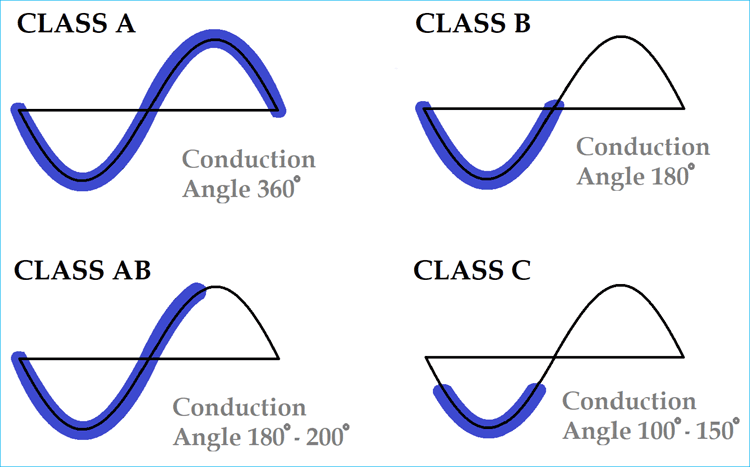
Classes Of Power Amplifiers Class A B Ab C D Amplifiers Explained

The Classes And Classification Of Amplifiers And Its Applications

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers

Class Ab And Class C Power Amplifiers

Class C Amplifier Working Principle Applications Advantages Disadvantages

Types Of Power Amplifier Classes Explained In Simple Words Homemade Circuit Projects